UX Design vs UI Design in 2023- The Differences
What is User Experience (UX)?
User Experience (UX) refers to the user's overall interaction and satisfaction while interacting with a product, service, or system. It includes every aspect of the user's interaction, including usability, accessibility, aesthetics, and overall experience.
Importance of User Experience in Design
User Experience is an integral part of design because it directly influences how users perceive and interact with a product.
A positive UX enhances user satisfaction, loyalty, and trust, while a poor UX can result in frustration, dissatisfaction, and, ultimately, a loss of users.
Designing with a focus on user experience guarantees that products are efficient and easy to use.
Evolution of User Experience
The field of User Experience has evolved, adapting to technological advancements and changing user needs. Initially, UX was mainly associated with usability, but it has expanded and now includes emotional and aesthetic aspects.
As technology has advanced, so has the complexity of designing user-friendly interfaces and experiences. In the B2B context, where transactions and interactions can be complex, the user experience plays a pivotal role in driving user adoption and satisfaction.
That’s why businesses now consider not only the functionality and usability but also the overall user experience, including emotional and aesthetic elements, when choosing B2B commerce platforms.
Foundations of UX Design
The history of UX design can be traced back to the early days of human-computer interaction, a time when there was no AI writer to help you generate text or create content. The concept gained familiarity with the start of personal computers in the 1980s.
Early efforts focused on improving the usability of interfaces. Over the years, UX design has combined insights from psychology, cognitive science, and other fields to create simpler, user-centered approaches.
Core Principles of Effective UX
- Usability: The product or system should be easy to use, allowing users to perform their goals with efficiency and minimal frustration.
- Accessibility: Design should be available to users of all abilities, ensuring that the product is usable by individuals with disabilities.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent design throughout the product to create a predictable and familiar user experience.
- Clarity: Clearly communicate information, functions, and feedback to users, minimizing confusion and misunderstandings. Use reliable communication channels, including cloud phones and real-time messaging platforms, to ensure a clear and effective exchange of information.
- Feedback and Response Time: Provide timely feedback to user actions, helping them understand the system's response and reducing uncertainty.
- Aesthetics: Consider the visual design and overall UI to create an appealing and engaging user experience.
- User-Centered Design: Involve users in the design process, understanding their needs, preferences, and behaviors to create a more user-centric product.
By sticking to these foundational principles, UX designers can create products that meet user needs and exceed expectations in terms of usability and overall satisfaction.
Emerging Trends in UX Design
Integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
The development of UX design extends to the integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), providing users with a wide range of interactive experiences.
AR and VR technologies can seamlessly enhance user engagement by blending the digital and physical worlds.
3D designs
In the design industry, 3D elements are increasingly being used. The incorporation of 3D designs adds depth and realism to user interfaces, creating visually compelling experiences.
A unique application of this trend is evident in the rise of 3D logo animation, where brands take advantage of dynamic visuals to enhance their identity.
Inclusive Design and Accessibility
As UX design evolves, there is a growing focus on inclusive design and accessibility.
Designers aim to create interfaces that are accessible to a diverse range of users, ensuring that everyone, regardless of abilities or disabilities, can access and seamlessly navigate through the website.
AI-generated content
The integration of AI-generated content is revolutionizing the way information is presented and consumed.
UX designers now have the option to create dynamic and personalized content, whether it's for websites, applications, or even advertising. This includes the ability to create ads that adapt to user preferences and behaviors.
Dark Mode
Dark mode has become viral as a user interface option, providing users with a visually comfortable and aesthetically pleasing.
This trend is not only aesthetically pleasing but also contributes to reducing eye strain, especially during extended periods of device usage.
Advanced Cursor Interactions
Innovations in cursor interactions are improving user engagement and navigation. Advanced cursor interactions go beyond traditional mouse movements, incorporating gestures and responsive elements to create a more intuitive user experience.
Incorporating these trends, UX designers can stay on top of industry advancements, creating experiences that are not only visually appealing but also highly functional and inclusive.
Cross-Platform User Experiences
Designing Cohesive Experiences Across Devices
Creating a seamless and consistent user experience across devices has become a central objective. Designing cohesive experiences requires a structured approach to ensure users can navigate effortlessly between devices while maintaining a smooth interaction.
Consistency is crucial in shaping a positive and memorable User Experience (UX). Many elements that shape consistency are fundamental parts that contribute to the overall cohesiveness and effectiveness of a design.
Why is Consistency so Important?
Recognition and Familiarity:
Consistency in design ensures that users experience a familiar interface across various landing pages. This recognition helps build a sense of familiarity, making users feel comfortable navigating different sections of a product or website.
Ease of Use:
Consistent design patterns and interactions make it easier for users to understand how to navigate and interact with a product. When users face a similar layout or flow, they can anticipate the placement of elements, reducing cognitive load and enhancing usability.
Building Trust:
Consistency in design enables a sense of reliability and professionalism. Users are more likely to trust a product or service that maintains a cohesive appearance, as it implies attention to detail and a commitment to quality.
Brand Recognition Across Platforms:
In the era of multi-platform experiences, maintaining a consistent UX across various devices and channels is essential. Users should seamlessly transition from a website to a mobile app, for example, without experiencing a harsh shift in design.
Enhanced User Engagement:
A consistent and well-branded UX contributes to enhanced user engagement. When users have positive and predictable interactions with a product, they are more likely to spend time exploring its features and functionalities.
Strong branding creates an emotional connection with users. A brand that consistently communicates its values and personality through its UX design can evoke positive emotions, leading to increased user loyalty and advocacy.
When it comes to online branding, particularly on Instagram, it becomes essential to not only maintain a cohesive brand identity but also actively manage Instagram accounts to engage with the audience effectively and amplify the emotional resonance established through UX design.
Maintaining consistency in design and integrating strong branding elements is not just about aesthetics; it's a strategic approach to creating a cohesive and memorable user experience.
By doing so, designers can build trust, foster brand loyalty, and ultimately contribute to the success of a product or service in the competitive field.
Responsive Design
Responsive design continues to be fundamental, ensuring that digital interfaces adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and devices. This approach remains crucial for providing a consistent and user-friendly experience across different platforms.
Challenges and Strategies
Navigating the challenges of cross-platform UX design involves addressing variations in screen sizes, operating systems, and input methods. Strategies include:
- Adopting responsive design principles.
- Utilizing adaptive layouts.
- Prioritizing content hierarchy to optimize the user experience regardless of the device.
Strategies for Enhancing User Engagement
Microinteractions
Microinteractions, subtle yet meaningful design details, play a crucial role in enhancing user engagement.
These small interactions contribute to a positive user experience by providing feedback, guiding users through processes, and adding an element of fun to the overall interaction.
Gamification and Interactive Elements
Incorporating gamification principles and interactive elements can significantly boost user engagement.
Gamified elements, such as rewards, challenges, and progress tracking, create a more immersive and enjoyable experience, encouraging users to interact with the platform and enabling a sense of achievement.
User-Centric Design Thinking
User-centric design thinking involves empathizing with users, defining their needs, coming up with solutions, prototyping, and testing.
This approach places the user at the core of the design process, ensuring that products and experiences meet their expectations and address real-world challenges.
Incorporating Feedback for Continuous Improvement
To achieve continuous improvement, integrating feedback into the design process is essential.
Regularly gathering user feedback through surveys, usability testing, and analytics allows designers to identify areas for improvement and refine their solutions based on real user experiences.
UX in Emerging Technologies
The Impact of AI and Machine Learning on UX
As technology advances, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is reshaping the landscape of user experience.
AI enhances personalization, automates decision-making processes, and adapts interfaces based on user behavior. Understanding the impact of these technologies is crucial for designing intuitive user experiences.
Integrating UX Design in Internet of Things (IoT) Products
The Internet of Things (IoT) brings something new to UX design, where connected devices and smart ecosystems demand thoughtful consideration. Designing for IoT involves:
- Creating seamless interactions between devices.
- Prioritizing user control and privacy.
- Ensuring a cohesive user experience across a network of interconnected products.
This integration requires a special approach to UX design to address the unique challenges posed by the IoT.
The evolution of UX design has passed a fascinating journey, from its early roots in human-computer interaction to the current era of AI, machine learning, and IoT.
In the fast-changing field of UX design, staying up-to-date on trends and technologies is essential. Key takeaways for UX designers in 2024 include embracing AI and machine learning, adapting to challenges and opportunities, and maintaining a strong commitment to user-centric design principles.
Have you ever stopped to wonder: “what do those terms UX and UI mean?” Believe it or not, even people who deal with design daily can confuse the two. As UXPlanet explains it: “User Experience and User Interface are some of the most confused and misused terms in the field”.
This is not a secret language that you can't get information on. Phrases such as “great UX” and “bad UI” of a design are not slang that others use. These are used to describe the two most important things that make a website a success – or a failure.
If you wish to learn what the two mean and how they are different, you’ve come to the right place.
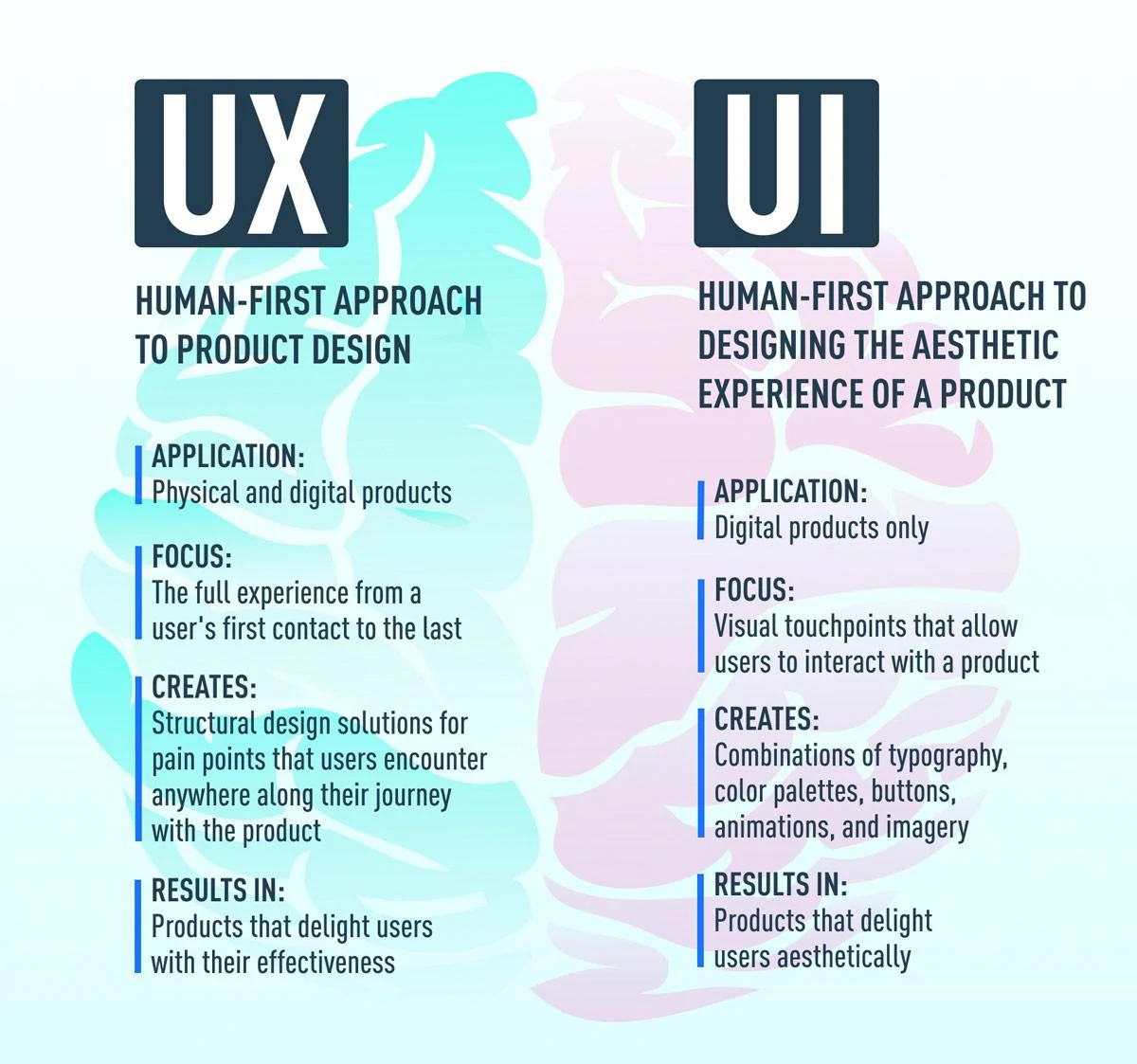
Defining UX and UI
Let’s begin by defining what these two terms mean.
UI, or user interface, is anything that users interact with when using a design, digital product, or service. This term captures everything from sounds, lights, screens, keyboards, and behaviors.
To understand it better, we should go back to when it all started.
In the 1970s, people used a command-line interface when using a computer. It all began with the programming language and those confusing lines of codes, required to complete the simplest of tasks we do with ease nowadays. It was soon after this that a new invention changed technology altogether – the first graphical user interface. From this point forward, people could interact with computers by using icons, menus, and buttons. This certainly made things easier.
It was at that point that the computer revolution began. Since then, designers have been putting all of their efforts into creating interfaces with the user in mind. If they didn’t do this, their products wouldn’t sell.
Now that the technology world has advanced beyond anyone’s predictions in the past, the role of the UI designer is more widespread and demanding. They also have amazing opportunities to craft unique designs and make use of modern technology to boost the interface.
However, they could never achieve success without a good user experience.
Maze, a leader in user testing and a popular tool among designers, has come up with a great guide on UI design. In this guide, they introduce a rather refreshing explanation of the difference between UI and UX: “If you were designing a house, UX would be the foundation, while UI would be the paint and furniture”. Thankfully, it is tools like these that make both UX and UI designing easier on the experts.
So, what is UX?
UX, or user experience, has evolved just alongside UI improvements. It's how people feel about the interactions with technology – whether positive, neutral, or negative. Naturally, designs that provide users with a quality experience are considered successful.
The term user experience dates back to the 1990s when Don Norman, a cognitive scientist employed by Apple at the time, defined it as follows:
“'User experience' encompasses all aspects of the end-users interaction with the company, its services, and its products.”
This is now considered to be a very broad definition, but it captures everything that UX does – because it does so much for the design. Any experience that people have with the design of a product or service, whether digital or otherwise, falls under this term.
In other words, UX is all about:
- How your users discover the product/ service
- Which actions they take while interacting with your interface
- How they feel and what they think during that time
- Impressions they take once the interaction is completed
The role of a UX designer is to ensure that the design meets the needs of consumers and to ensure that they achieve the desired outcome in the simplest, most seamless way.
UX and UI cannot thrive without the other, which is why understanding the difference between the two is essential for designers.
The Difference Between UI and UX
On a basic level, UI includes all the elements that enable people to interact with the service or product in question. UX, on a basic level, is what that same user takes away from the experience. Both have a huge effect on the behavior of the user – and the future of the design.
CareerFoundry visual on this is quite enlightening:
Let’s take one simple example to describe all this. We all know and love Google – it’s the place where we go to get our information. The founders of this search engine knew exactly what to do – create a simple place where people can get what they need. Just about anything you need to know, you can get the information in the blink of an eye with this engine.
However, what happens if getting that information takes too long every time you try to learn something? If it took, let’s say, 20 seconds to get your results – would you be willing to keep searching?
Google has a pretty straightforward and simple interface, which is what makes it so desired by users seeking information. It's as simple as it gets – you open it, type what you need, and click on search. But, if the interface remained this way, but it took too long to get the information, the experience of users would be worse.

According to this Medium article and the words of Miller, a web developer, “UI is the saddle, the stirrups, and the reins. UX is the feeling you get being able to ride the horse”.
So, these two terms might not be the same thing, but they go hand-in-hand. None exists without the other. You need UI to have UX, and vice versa. This is why a great designer possesses both UX and UI skills, even if they are focused on only one.
How the Two Work Together
Now that you know how they differ, it’s time to learn how to use both to achieve your goals.
This starts with the UX designer’s work. The designer considers the journey of the user from start to finish. He thinks of the steps users take to solve a particular problem, which tasks they'll be asked to complete, and what they feel and behave like while they do all this.
Most of the time, UX designers with the help of a professional agency like RCCO explore and define the pain points that users come up against, and try to find the best strategies to improve their experience. This is all based on extensive user research that defines the target audience, the behavior of current and past users, and predictions on how to make them happier with the design.
Once this is done, the UX designer maps out the journey of the user across the product, considering information architecture, features, etc.
When the skeleton is all mapped out, the task of the UI designer begins. His job is to bring all this to life and make it accessible to the user. Without UI, users won’t be able to enjoy the experience that the UX designer prepared for them.
UI designers take into consideration the data collected by the UX designer to create the interface. They’ll include the individual touchpoints and screens that users will encounter, consider the better option for providing the information, and focus on other details that make the journey possible.
Many ask the question: “Which one is more important”?
The answer is – none. Both these are very crucial in the designing process. If the design looks good, but it is difficult to use, its UX is poor and its UI is great. When the design is usable, but it looks devastating, it’s the very opposite. Neither of these situations is good.
Even if a product works with only one of these elements being optimized, imagine this: how great would it be if it optimized both?
One Common Element: Research in UI and UX Design
Both UI and UX design are based on one thing – research. This is an invaluable step of both and is what determines the success of the product. For a product to be successful, UX and UI experts need to gather tons of accurate information. This information will tell them what the user wants or expects from the product, as well as how they want it.
Research including analytics and testing with tools such as Maze provides invaluable insight into the user's expectations and needs. Based on this, designers can make informed and safer decisions.
How do UX experts research?
Some of the methods used to collect the necessary information include research of user or target persona, conducting user interviews and surveys, or using focus groups to gather information.
And what about UI designers’ research?
UI designers will work closely with UX experts to check the research results, learn more about the audience, and make informed decisions on fonts, colors, visual elements, patterns, and more.

Final Thoughts
Hopefully, at this point, you understand the strong line between UI and UX design. They are different even though they go hand-in-hand and are important for the product. Whichever you choose to pursue, you should gather as much knowledge as you can about the other, and collaborate with other designers to achieve the best results.
Recommended Posts

12 Best Google Chrome Screenshot Extensions for 2025
July 30, 2024
10 Best Web3 Design Agencies in 2025
July 30, 2024

Understanding Website Content Security Policy in 2024
January 10, 2024