How to Build the Perfect Website: Ultimate Strategy
In this article we are going to describe how to build the perfect website and make its architecture & SEO up and running to get the most benefits out of it.
Build the Perfect Website & A Guide to Website Architecture for SEO Beginners
Are you trying to climb the search engine ranking pages (SERPs) and struggling to find an article with solid SEO advice? Hundreds of marketers and small business owners are in the same boat as you.
In this article, you will learn how to build a search engine optimized website from the get-go.
As the biggest and most widely used search engine, your goal is to bag one of the top positions on Google’s results page. But Google updates their algorithm multiple times a year.
Most of the guides you’ve read are probably outdated and even if they weren’t you don’t know the first thing about coding or have the budget for an SEO agency.
This article doesn’t suggest any black hat SEO tactics. Everything we will cover will give you an honest approach to your strategy.
Website architecture should be the first thing that you optimize.
It’s incredibly straightforward and easy to maintain.
Why is Website Architecture Important?
A good website structure, or architecture, will help Google when it comes to crawling and indexing your site.
To choose which URL’s to display on the SERP, the search engine needs to be able to locate your site (known as crawling) and categorize it according to the content available (known as indexing).
Poor site architecture could interrupt either of these stages.
Your site might end up in the wrong category and will never rank for targeted keywords.
Or, in the worst-case scenario, the search engine won’t be able to find your website and will never know it exists.
We have wrote another comprehensive article about improving WP SEO, feel free to check it out: Improve WordPress SEO: 11 Tips to Boost Website Rankings
NOT an Overnight Fix
Of course, website architecture is just one element of the lucrative SEO strategy.
Don’t think that ticking all of these boxes will get you onto page one of Google.
It will help your SEO, but you still need to work on your off-page SEO and your site’s content simultaneously. Furthermore, there is no overnight fix.
Search engine optimization is a constant process.
Do not tick these boxes and then leave your perfectly architected site to rot.
SEO agencies exist because their job is a constant process.
This article will help you identify things that you can do yourself, without the extortionate agency fees.
Quadrant2Design, an exhibition stand design consultancy in the UK, has a team of people working on SEO while their industry is shut down.
None of them are experts, but the results that they’ve seen in the last six months are mind-blowing.
What is Website Architecture?
The definition of architecture is:
“The complex or carefully designed structure or something”
And that is exactly what we are referring to when we talk about website architecture.
Much like a building, a website should never be thrown together with no plan.
Good website architecture offers a layout that enhances the user experience (UX) and allows crawl bots to easily interpret the content.
Too many SEO agencies spend your money building a strong link-profile and editing on-page content.
If you want to stand a chance of ranking in SERPs, you need to build a solid foundation.
Luckily, website architecture is easy to get right.
Even with the most basic knowledge, you will be able to implement these tactics on any site.
For now, forget about your link-building and content marketing campaigns. That can come later.
This article will help you optimize your website for search engines from the bottom, up.
Let’s build a solid foundation.
Crawl of Duty
First thing’s first, do you understand how and why search engines choose the results that they display on search results pages? This is key to designing your website architecture.
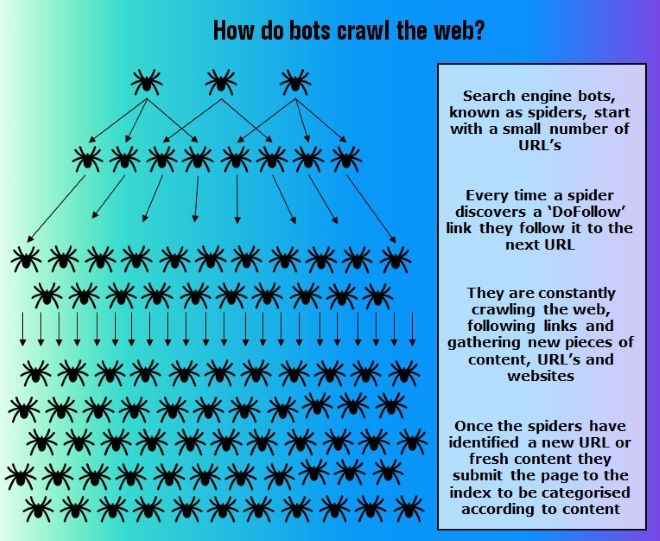
Spiders
Every second, thousands of ‘bots’ crawl the internet looking for new pieces of content, URL’s or entire websites.
These bots are known as crawlers or spiders.
Why spiders? Because they essentially crawl the internet by following links and building the web.
Each spider starts with just a handful of the most prominent URL’s.
They crawl the content on these pages and jump to other sites each time they come across a new ‘DoFollow’ link.
Every time they discover fresh content it gets submitted to the index.
The spiders pull all of the information off of the page and store it all in a huge database (aka index).
This is the information that the search engines use to build the ranking pages.
How easy is your website to find, crawl, and index?
Menu
Make sure your menu is easy to use and does its job properly.
Your website navigation needs to be clear, simple, and practical.
Break your site down into identifiable categories.
This helps the spiders to crawl your site and enhances the UX.
If you have a complicated site layout, you need to be using Deep Theme, by Webnus.
It helps you to create an advanced mega menu allowing you to easily guide users and crawl bots around your site.
Site Map
Ever wondered why websites have a ‘site map’.
There doesn’t seem to be any need for it from a user’s perspective. But there is for a spider.
Remember, as spiders crawl the web they are following every ‘DoFollow’ link that they come across.
A site map allows you to place a link to every page of your site, on every page of your site.
This is an easy way to make sure every page of your website gets crawled, indexed, and ranked.
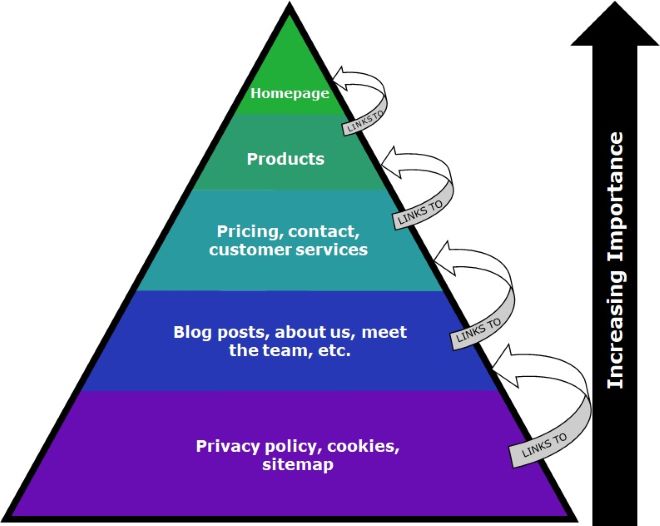
Internal Linking
The other thing that you need to do to speed up this process is to incorporate a structured internal linking system.
A site map helps to get everything done quicker, but it doesn’t help spiders identify the hierarchy of your website’s pages or enhance the UX.
Internal links, like this one which links to our homepage, aim to keep visitors on your site by recommending content that they might like.
You are also telling the spiders which pages are important.
Think about your website and try to organize the pages into a hierarchal pyramid.
You should be aiming for two-three internal links per page (and limiting the number of external links to stop the spiders leaving your site).
Start at the bottom of your hierarchy and link upwards.
The chart below shows you the best practice for your internal linking strategy:
Meta Tags
Unfortunately, search engines can’t employ thousands of people to crawl the internet.
That’s why spiders (crawl bots) exist.
However, they aren’t human. That’s why they need some clues as to what your content is about.
This section is sub-headed Meta tags, however, it covers a lot more than that.
Meta Title and Description
Of course, the Meta title and description are important.
These are the spider’s first indicators of what your content is about.
Secondly, they look at headings.
Your first heading should use a H1 tag and tell the spider exactly what your content is about.
Headers
After that, the headers should use H2 and H3 tags. Think of your website as an essay.
The structure should make sense in the same way.
One title, then chapter or sections that are divided into smaller categories.
It is amazing how many people use H1 tags for all of the headings.
This does not make spiders pay more attention. It makes them penalize you for keyword stuffing.
Image Attributes
Finally, images are a great place to tell spiders even more about your content.
The image title should explain exactly what the image shows.
For example, a photo of a Labrador puppy should be called Labrador_puppy.jpeg (not Canon763548_77.jpg).
Next, you need to add ALT tags to your image.
These display on your webpage if your image isn’t loading and also need to perfectly describe your image (but can be less techy).
Remember, Google can’t see your image – just the ALT tag.
Going back to the Labrador example, your ALT text might say: Cute Labrador Puppy Playing in grass.
These behind the scenes Meta tags give you a greater chance of getting indexed correctly, but of course, without being crawled first this won’t matter.
Make sure that every page of your website is easy to find and crawl.
And then boost your chances of ranking by helping the spiders index you correctly.
Deadliest Match
When we talk about duplicate content, we are referring to content that appears in multiple URL’s.
The problem with this is that search engines have to try and trace the source.
They don’t want the same piece of content filling up their ranking pages.
The main problem that search engines have with duplicate content is deciphering which pages to include/exclude from the index.
If the same content appears on multiple pages they don’t know where to direct the link metrics such as trust, authority. and link equity.
This is why copied content needs to be wiped from your site, but how did it get there and how can you fix it.
Scraping
If you run a blog on your website you might have been tempted to scrape the content of another influencer. We all feel like that sometimes.
Scraping is the term given to online content that closely resembles content found at another source.
A few words may have changed, but it’s duplicated.
Many people don’t realize that blogs aren’t the main target for this.
Product descriptions, about us pages, or author bios are great examples of this.
To find out if anyone has scraped content off of your site, use a free online plagiarism tool.
URL Variations
You could have duplicate content within your site, even without scraping or copying pages.
URL variations will often duplicate entire pages to create printer-friendly versions or track session IDs.
Try to avoid adding URL parameters where possible (this could help with site speed as well).
Too Many Prefix’s
Many business owners think that they should invest in every variation of their domain to gain authority.
This is good website practice unless you are duplicating content from one site to another.
If you have separate versions of your site (one with the ‘www.’ prefix and one without) use 301 redirects rather than duplicating the content.
The same can be said for HTTP:// and HTTPS://.
What Can You Do to Fix Duplicate Content?
If you discover duplicate content on your site and you can’t simply remove it there are other things you can do.
Firstly, set up 301 redirects on duplicate pages pointing to the original content.
This means you keep your inbound link juice and search engines know which page to add to their index.
Secondly, add canonical attributes to pages that contain the original content.
Sometimes you might have no choice but to use the same content on multiple pages.
A canonical attribute will tell the search engine that that page is a copy of a specified URL (thus, telling them where to find the source).
Finally, Meta Robot attributes can be added to any individual page and tell the spiders not to crawl or index that URL.
If your content has been scraped or copied but taking it down isn’t an option, a Meta Robot NoFollow tag will help your website architecture while you resolve the issue.
Assassins Speed
Page speed has been highlighted as one of the factors that influence Google’s ranking algorithm. Never underestimate its importance.
With over 200 ranking factors (that we are completely unaware of) we have to take full advantage of the ones that they let slip.
Page speed describes the length of time to fully display the content on a specific page.
Google expects this to be under two seconds but wants to see page speeds that match their own – under half a second.
How can you achieve this?
Optimize Images
When someone opens a webpage, that page loads everything in full before bringing it all back down to size.
Save your site the struggle by optimizing your images before you upload them.
Upload images in the correct size, and use jpeg’s to reduce the file size. This will save you time and reduce your page speed.
Optimize Your Code
To display any webpage, a browser has to read the code.
Save everyone some time by removing the spaces, commas, other unnecessary characters, formatting, unused code, and code comments.
Remove Render-Blocking JavaScript
To load a website, the browser reads the HTML and renders the information.
Funnily enough, it is a lot more technical than that but we did say this guide was for beginners.
To fully render the page, the browser builds a DOM tree using the HTML coding.
Some JavaScript functions, such as CSS, block the render process until the CSSOM is fully-constructed. This slows the page speed.
Google suggests avoiding all forms of render-blocking JavaScript.
Reduce Redirects
Think of redirects like bus stops.
If nobody wanted to get off or on your bus throughout your journey, the journey time would be much quicker. Each redirect is essentially a bus stop.
The browser sends the user to one URL only to find the redirect code and have to go to another.
If you are using redirects to save the link juice you’ve managed to collect, try to decide how important the links are.
Are they worth an extra second to your page speed? Remember, Google aims for half a second per page.
You can still have an effective web design and fast page speed.
Deep Theme, by Webnus, is high performance and super responsive.
This allows you to integrate complex design features into your website without harming the load speed.
Pop Structure
The URL that identifies your webpage is the first indication a visitor (and the spiders) has of your content.
It should let them know who you are and what information they are likely to find on that page.
According to MOZ, your URL should be made up of these seven elements:
Protocol | Subdomain | Domain | Top-Level Domain | Folders | Page | Named Anchor
Which will leave you with something like this:
[https://] [store.] [example.] [com/] [topic] [subtopic] [descriptive product name] [#top]But of course, there isn’t always a need for that much detail.
The majority of small businesses will only need a handful of those factors and can expect to see something like this:
[https://] [webnus.] [net/] [social-media-growth-fostered-a-remote-work-culture/]As you can see, the protocol, domain, TLD, and page were all elements of this domain.
It is clear, identifies what the content is about, and tells you who we are.
The URL structure is defining our website architecture.
But what else do you need to do?
Keyword Targeting
The first thing you want to do is make sure that the keyword you are trying to rank that page for is included in the URL.
In some instances this might be your domain, in others, it could be the page title.
The chances are you have already used your keyword in your H1 and it naturally fills its position in your URL.
Length
If your URL is longer than 2,083 characters then the page won’t be able to render in browsers.
You want to keep it much shorter than that.
With length, you are aiming to improve user experience.
You want your URL to look inviting when it is shared on social media. Keep it short and meaningful.
Whichever way you decide to structure your URLs, make sure you keep it consistent across your entire site.
Poison Cloak
Now you know what you’ve got to do to correct your website architecture for better SEO, but what must you avoid? Cloaking may not be as common as it once was, but you’d be surprised how many people get picked up for it.
Cloaking is the act of presenting different content to human visitors as you are to search engines. This was common practice before the Panda update.
In 2011, Google updated its algorithm to better identify the quality of the content available on any given web page.
Before the update, SEO experts would hide chunks of keyword-heavy text on a page by making it the same color as the background.
Users couldn’t see it, but the bots read it and indexed it as if it was part of the website.
This problem was quickly flattened and sites got penalized for trying to cheat the algorithm this way.
Then, as the SEO experts got smarter, they found more ways of cloaking. A good example is an image gallery on a website.
There is little content or editorial for the spiders to analyze, so how do you get that page to rank? People began hiding entire HTML documents on pages that were image heavy to boost their results on the SERP’s.
The search engines read and index this body of text as if it were any other web page, but the human users never get to see it.
This is a problem for the search engines because it messes with user experience.
The SERP’s aim to show an audience the most accurate and relevant content to answer their query.
Cloaking interrupts this process.
More often than not the user won’t be expecting or have any need for the content you are showing them.
The Perfect Website Architecture: A Summary
And that right there is everything you need to know about website architecture.
Building the foundations right is just as important as delivering valuable content regularly and accruing a strong backlink portfolio.
All of the tricks and tips we’ve shared in this guide are easy to implement and don’t require any expertise or SEO agency.
If you’ve noticed problems with your website, either falling down the SERP’s or losing organic traffic, your website architecture should be the first thing you fix.
Remember these points and you’ll soon strike SEO gold:
- Is my website easy for search bots to find?
- Is my web content easy to categorize?
- Do I have any duplicate content on my site?
- Is my site fast?
- Are my URLs properly formatted?
Saying yes to all of these questions but still not seeing an SEO benefit? Make sure that all the content on your site is available to both human users and search engine spiders.
It might not be an architectural issue, you may have been penalized for cloaking.
Recommended Posts

6 Steps to Start Your WordPress Website Without a Hitch
April 29, 2024